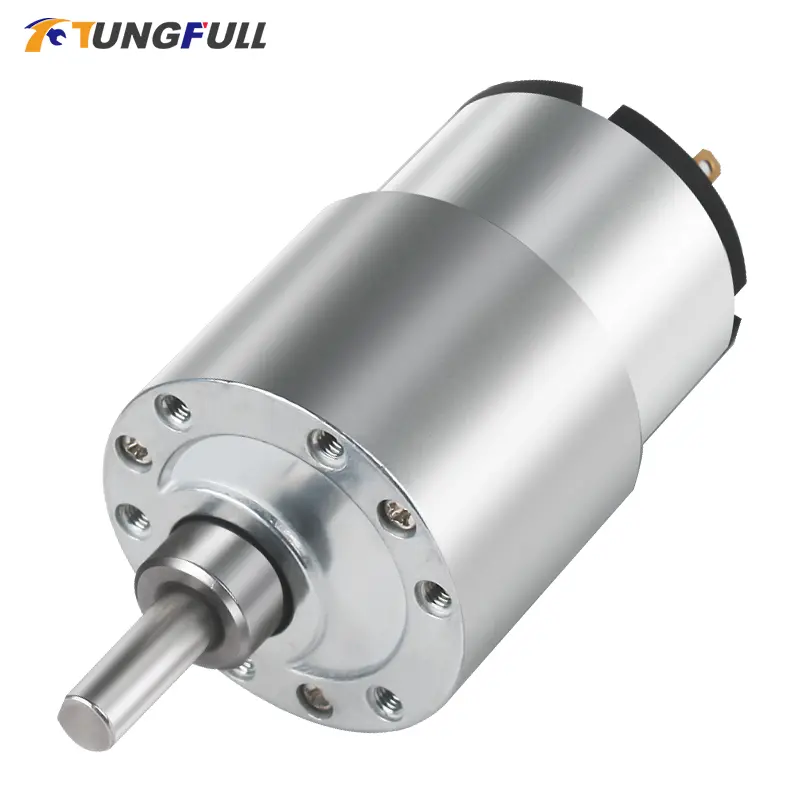
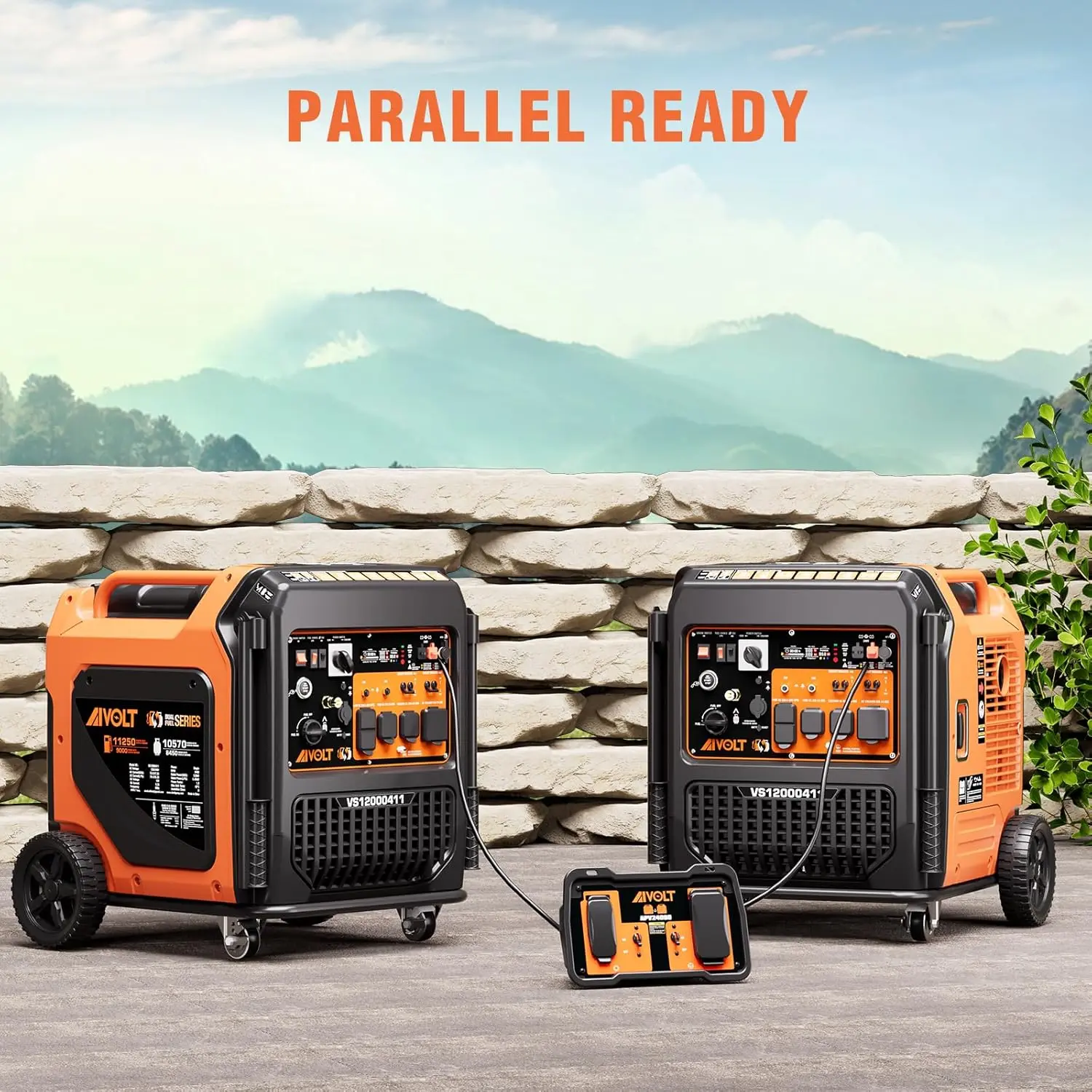
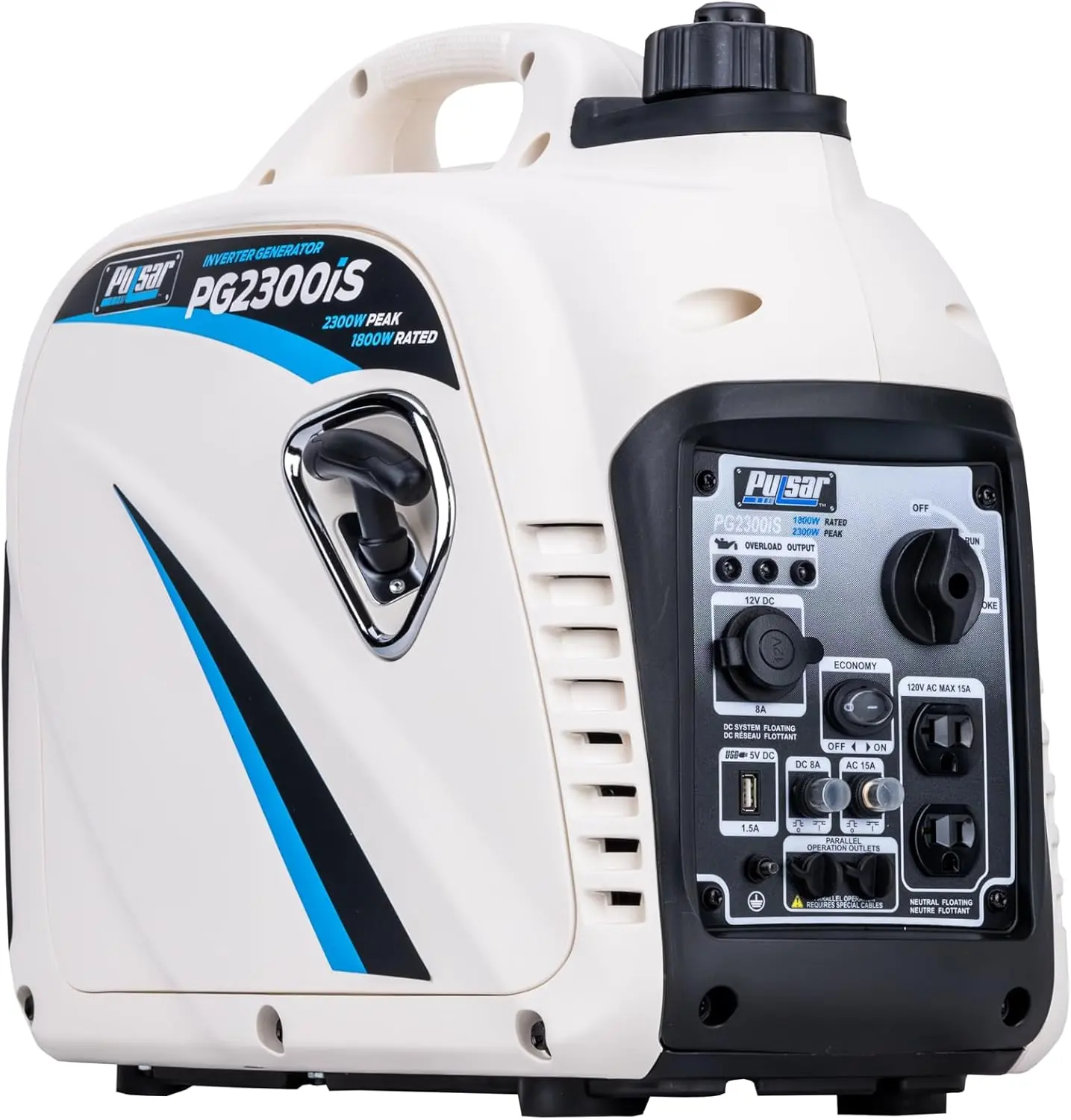
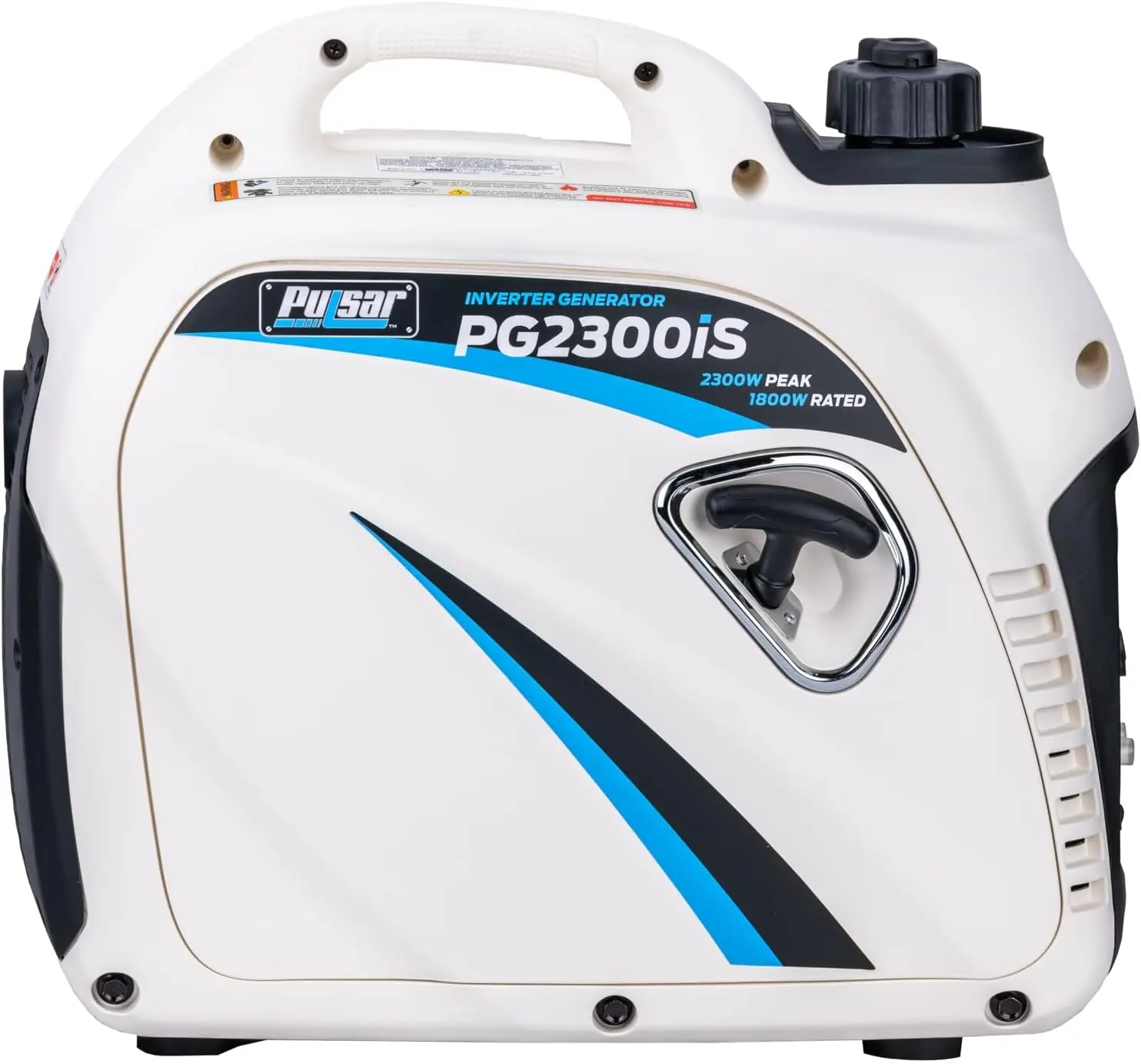
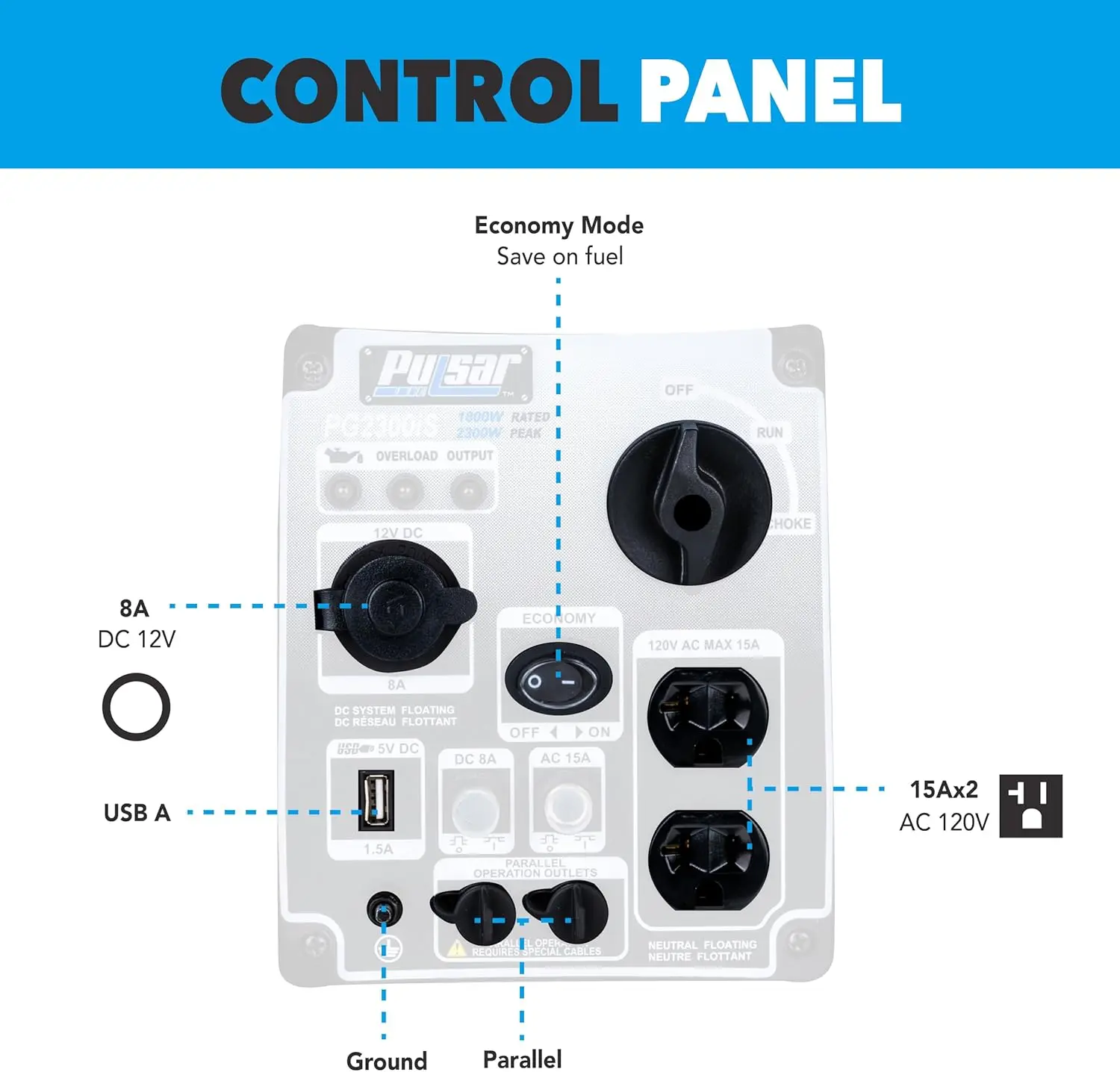
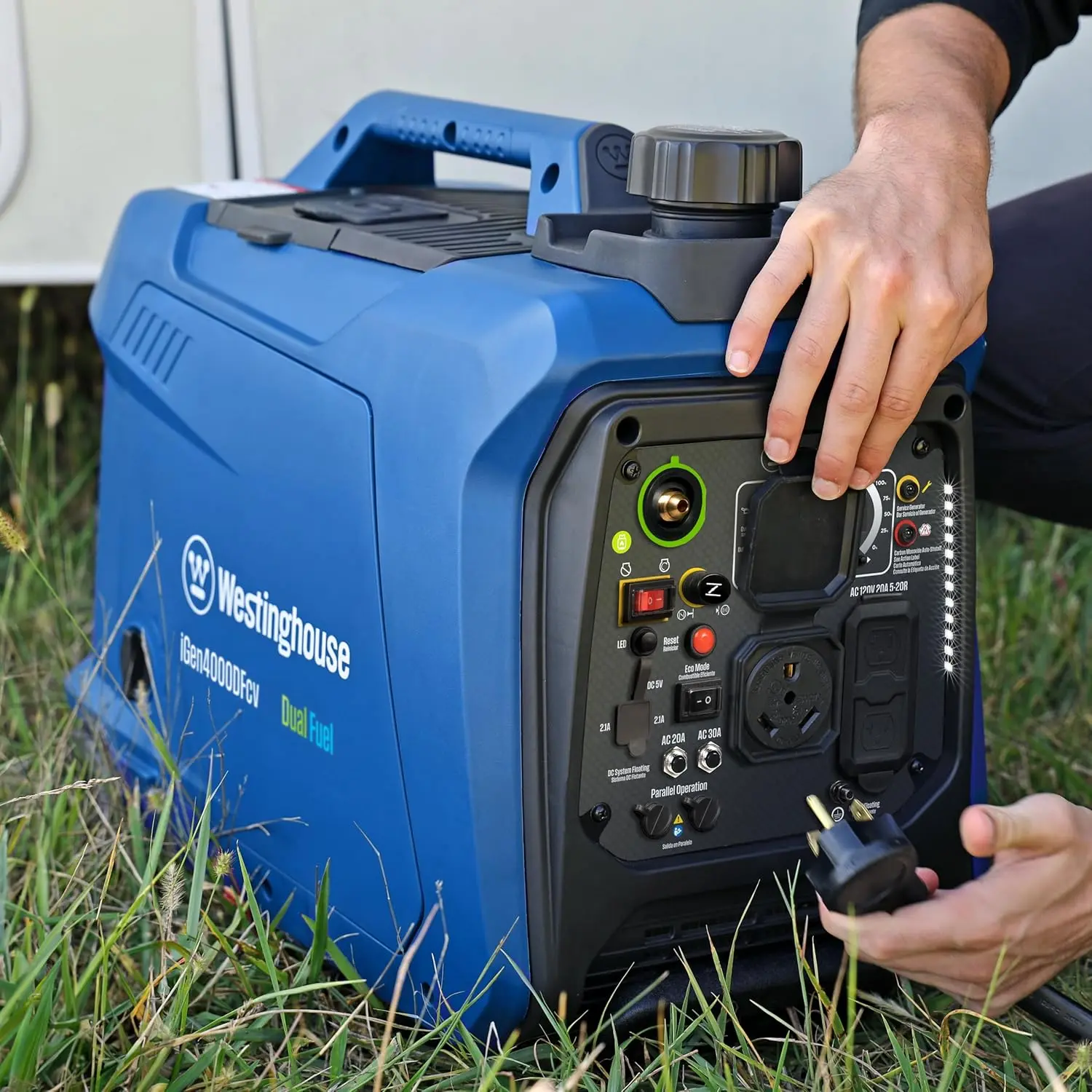
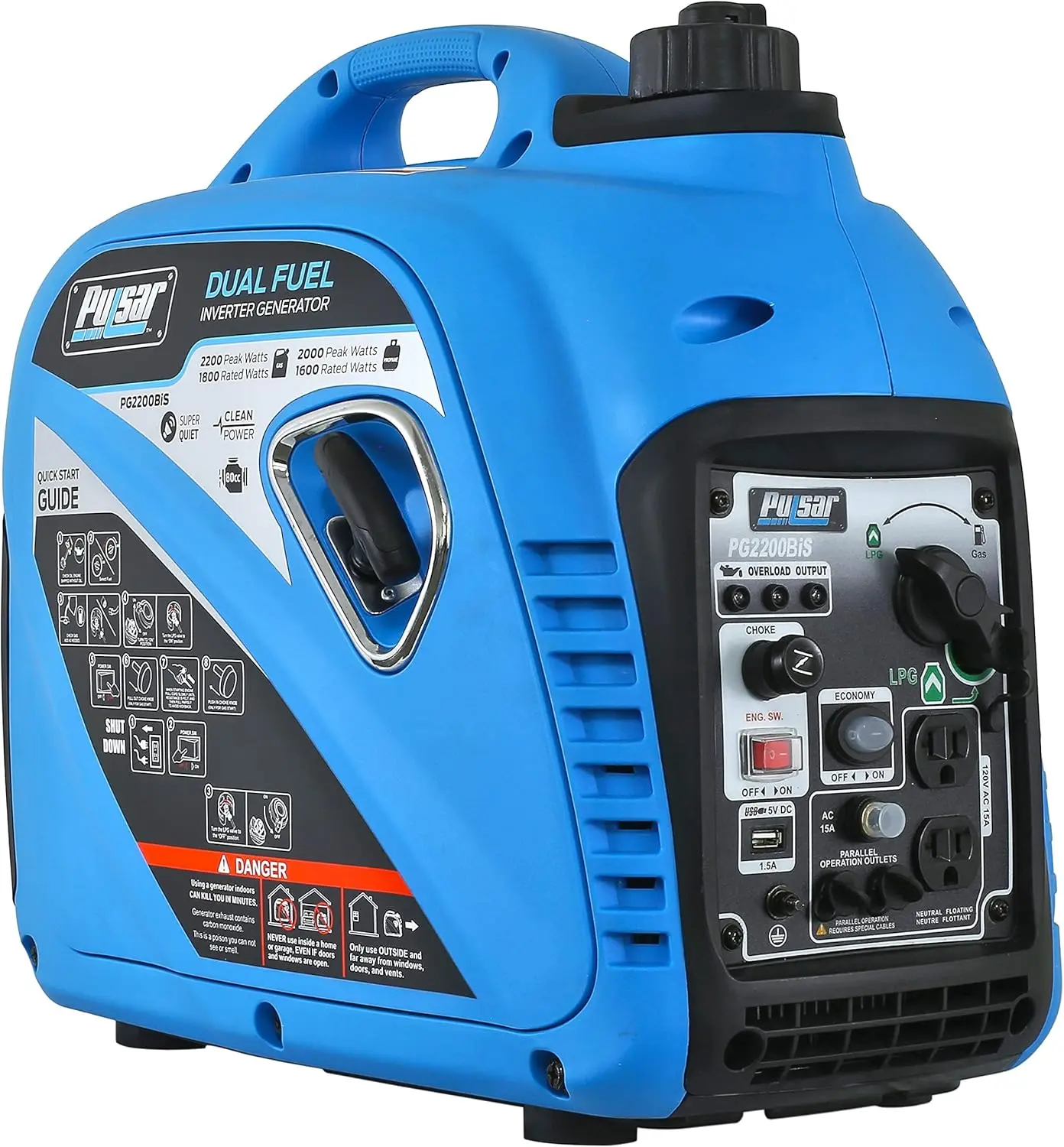
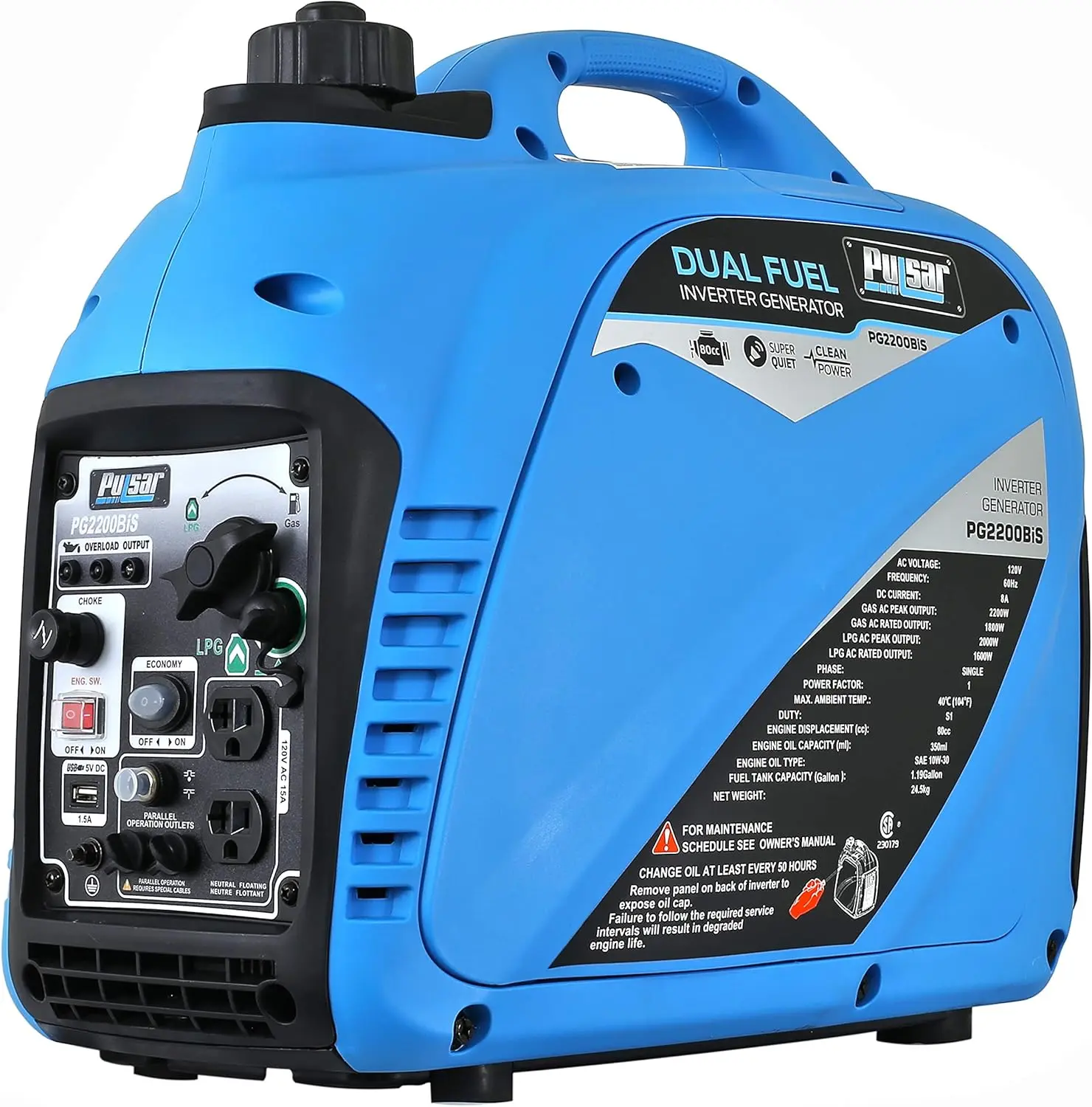
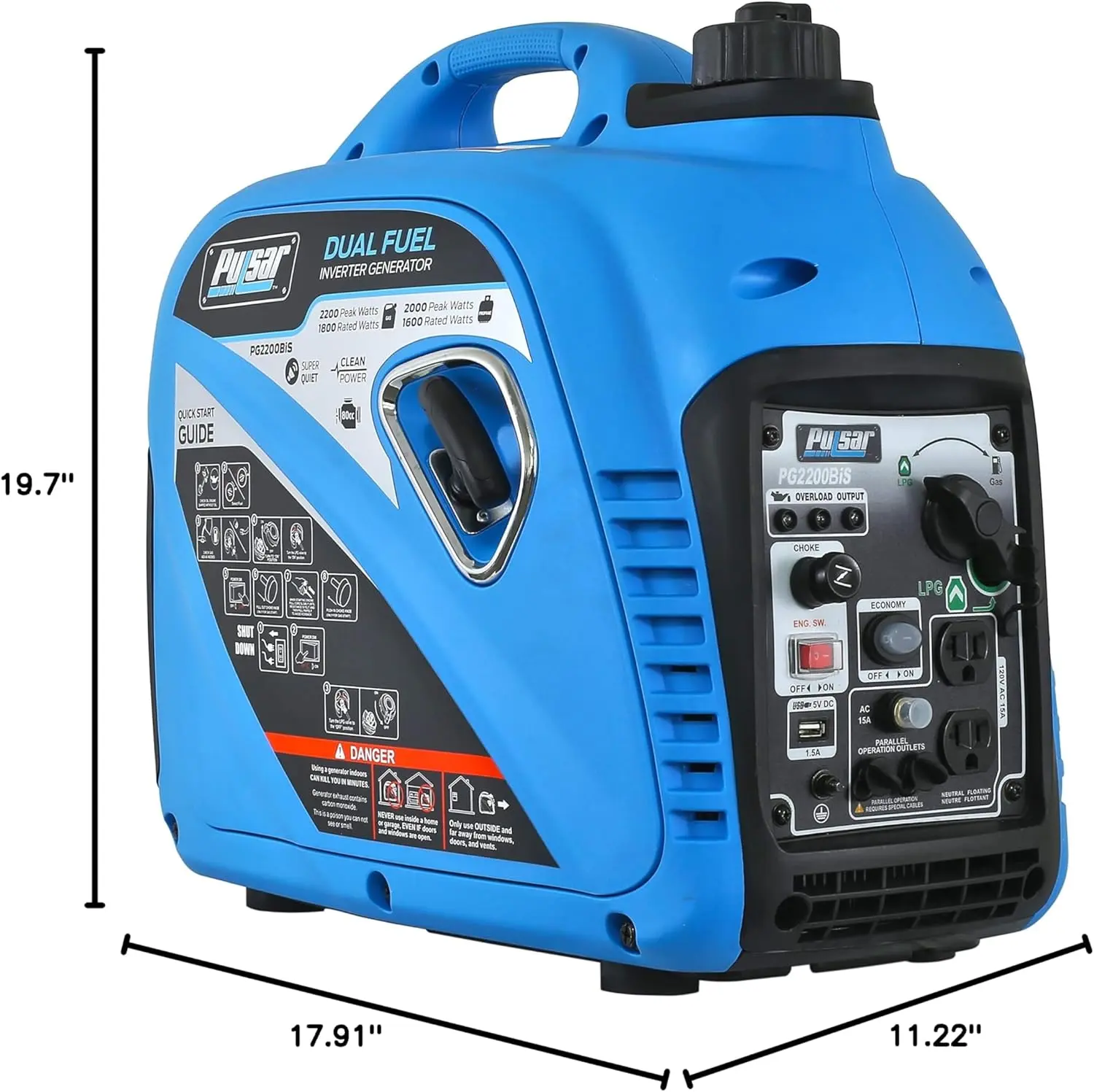
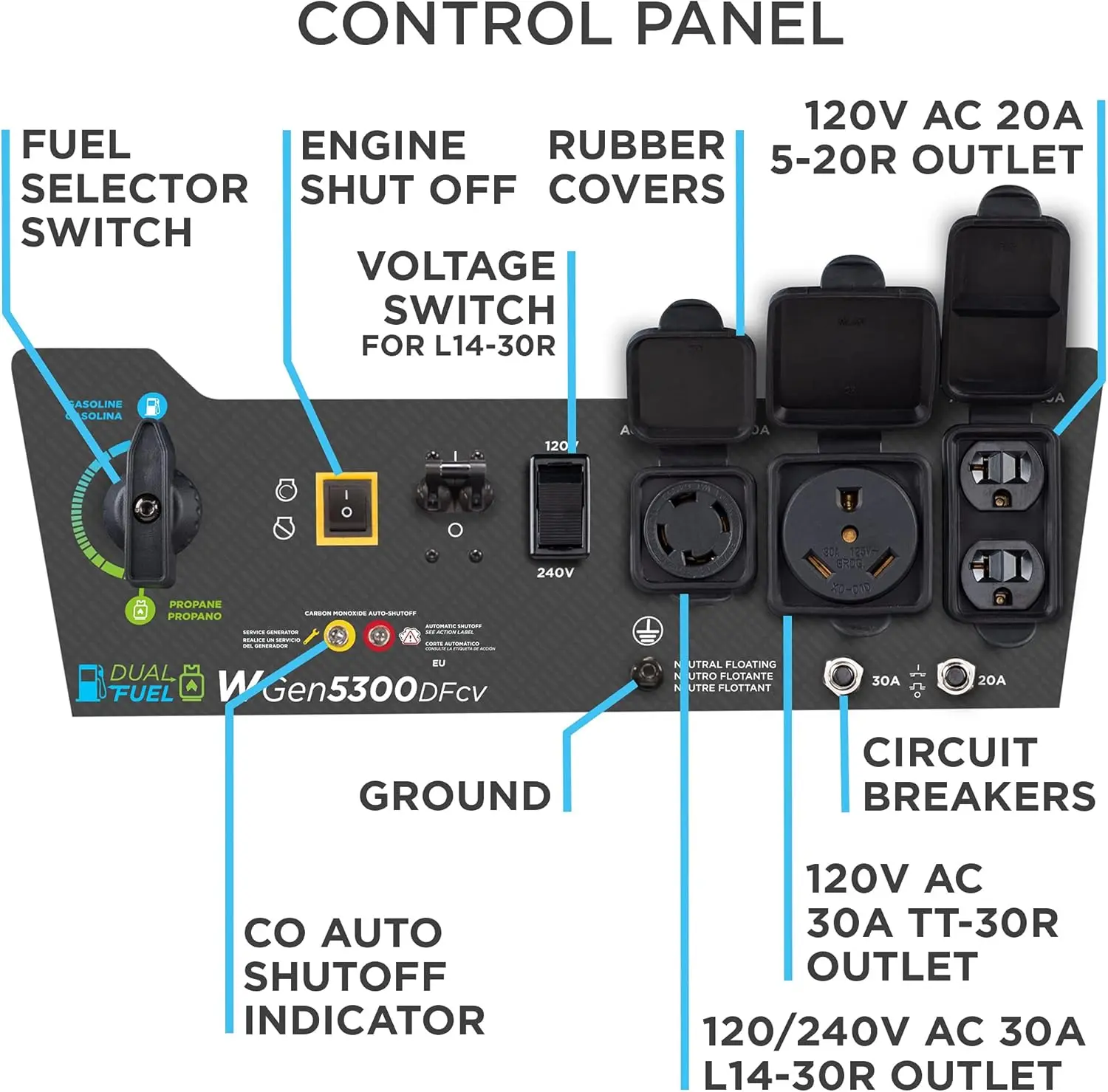
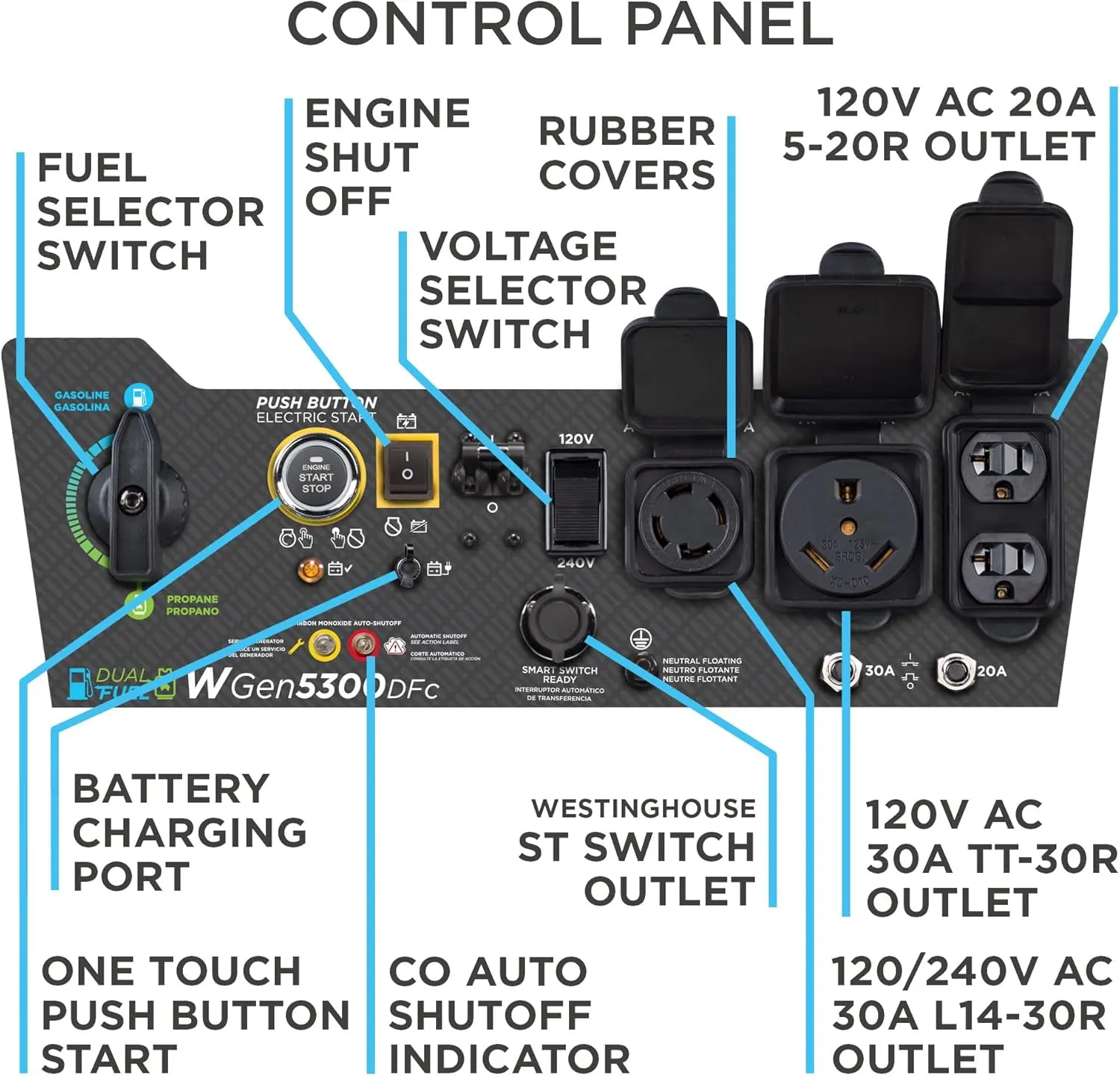
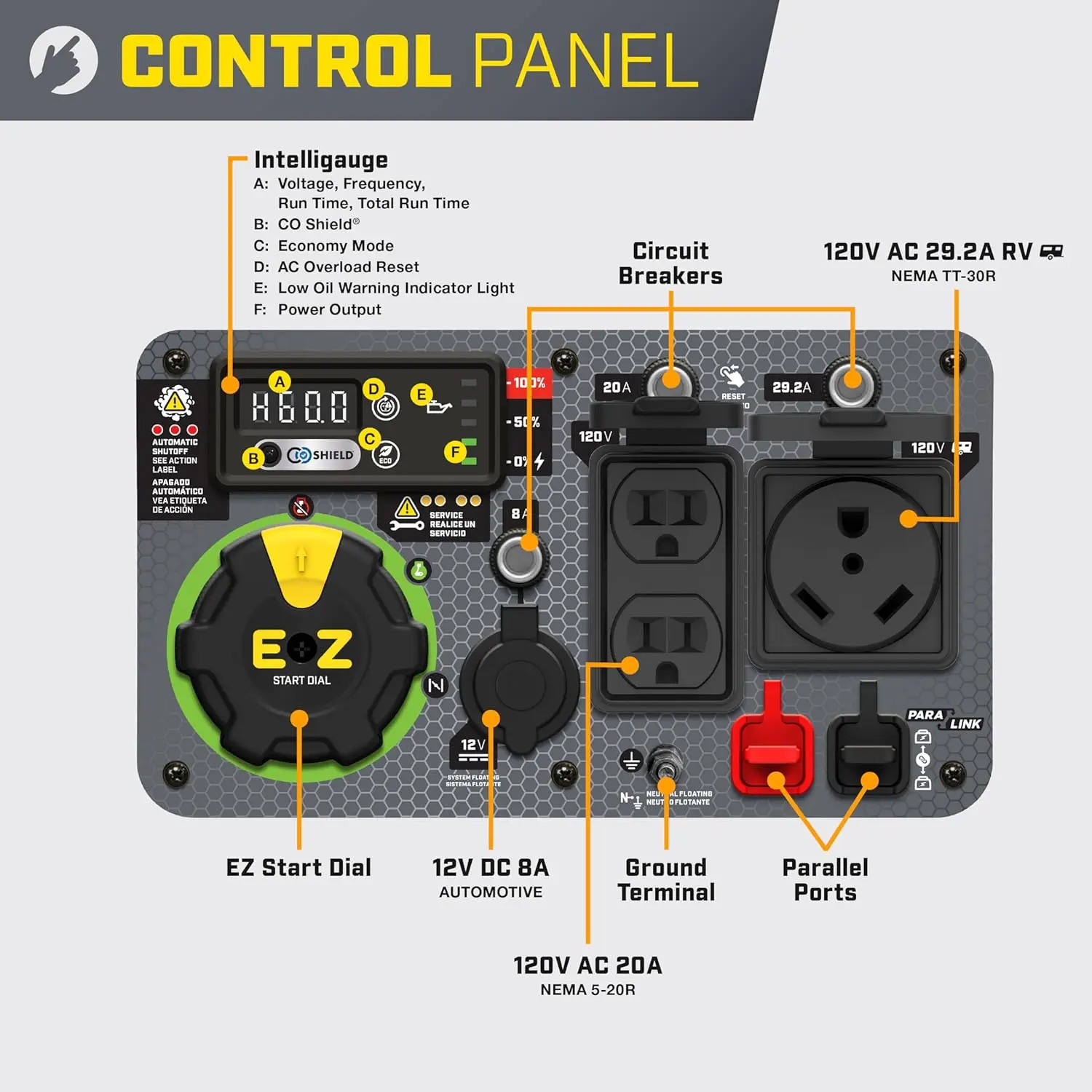
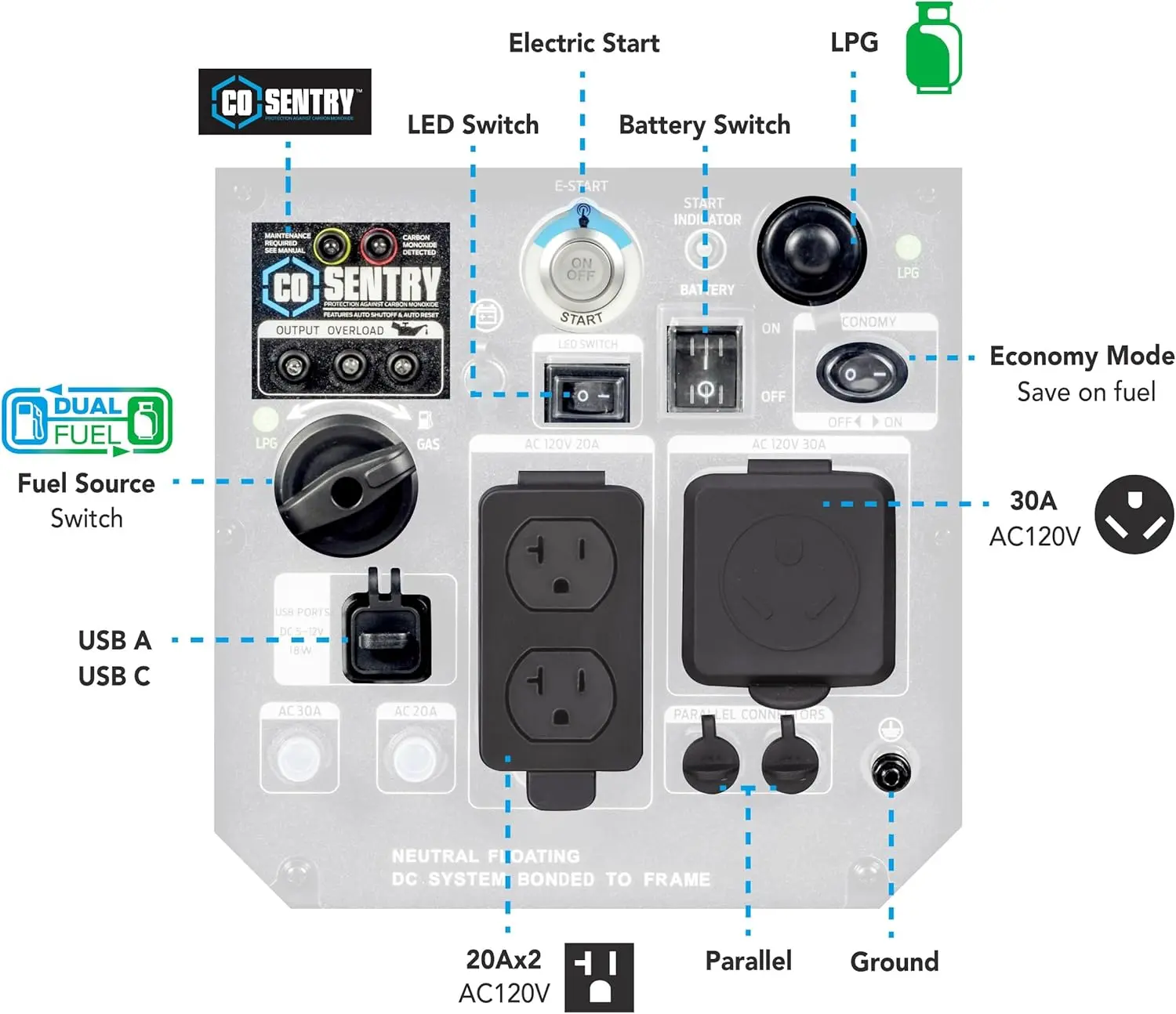
Reversible Electric Reduction Gear Motor DC 6V/12V/24V 7RPM to 960RPM High Torque Gearbox JGB37-520
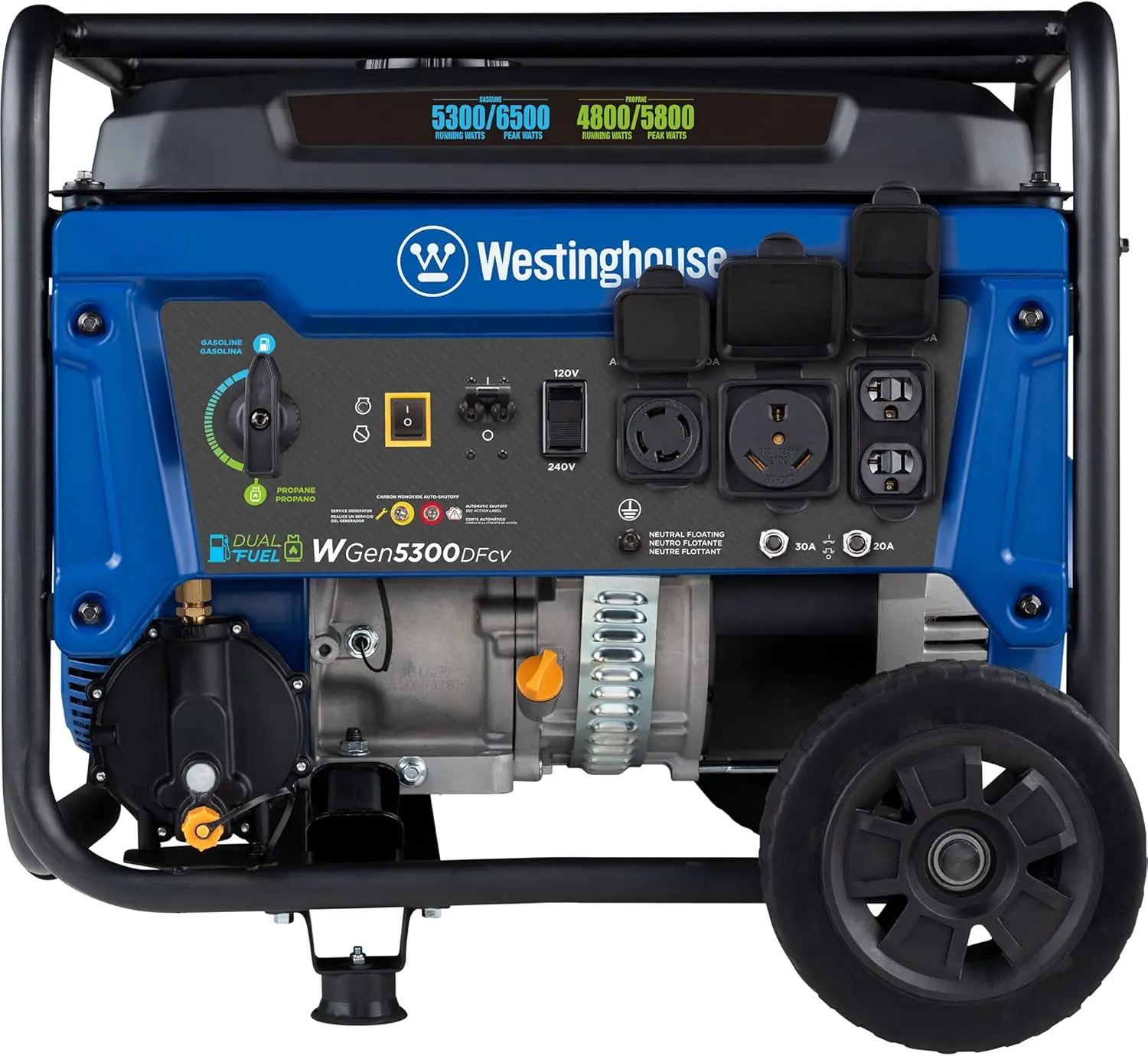
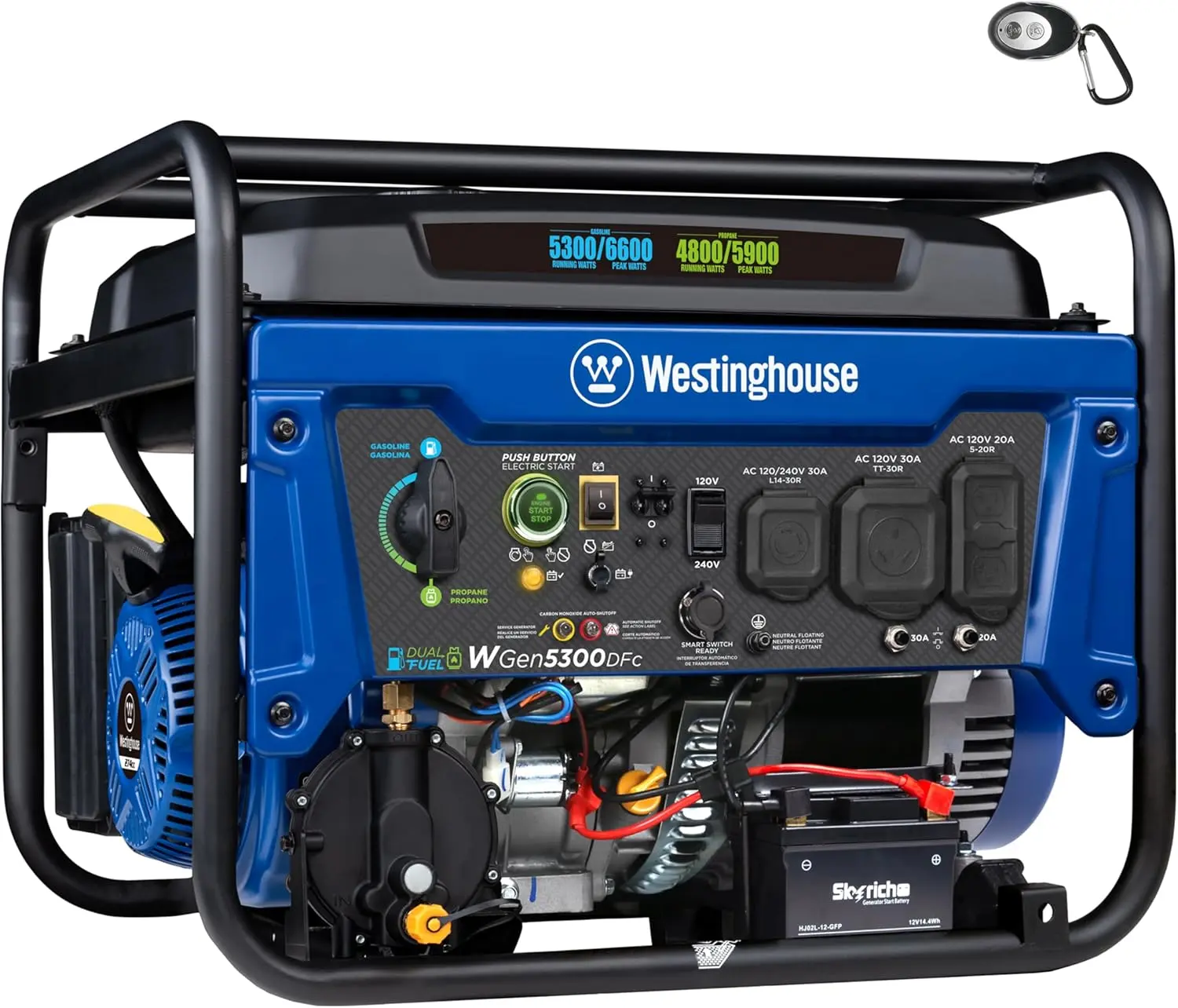
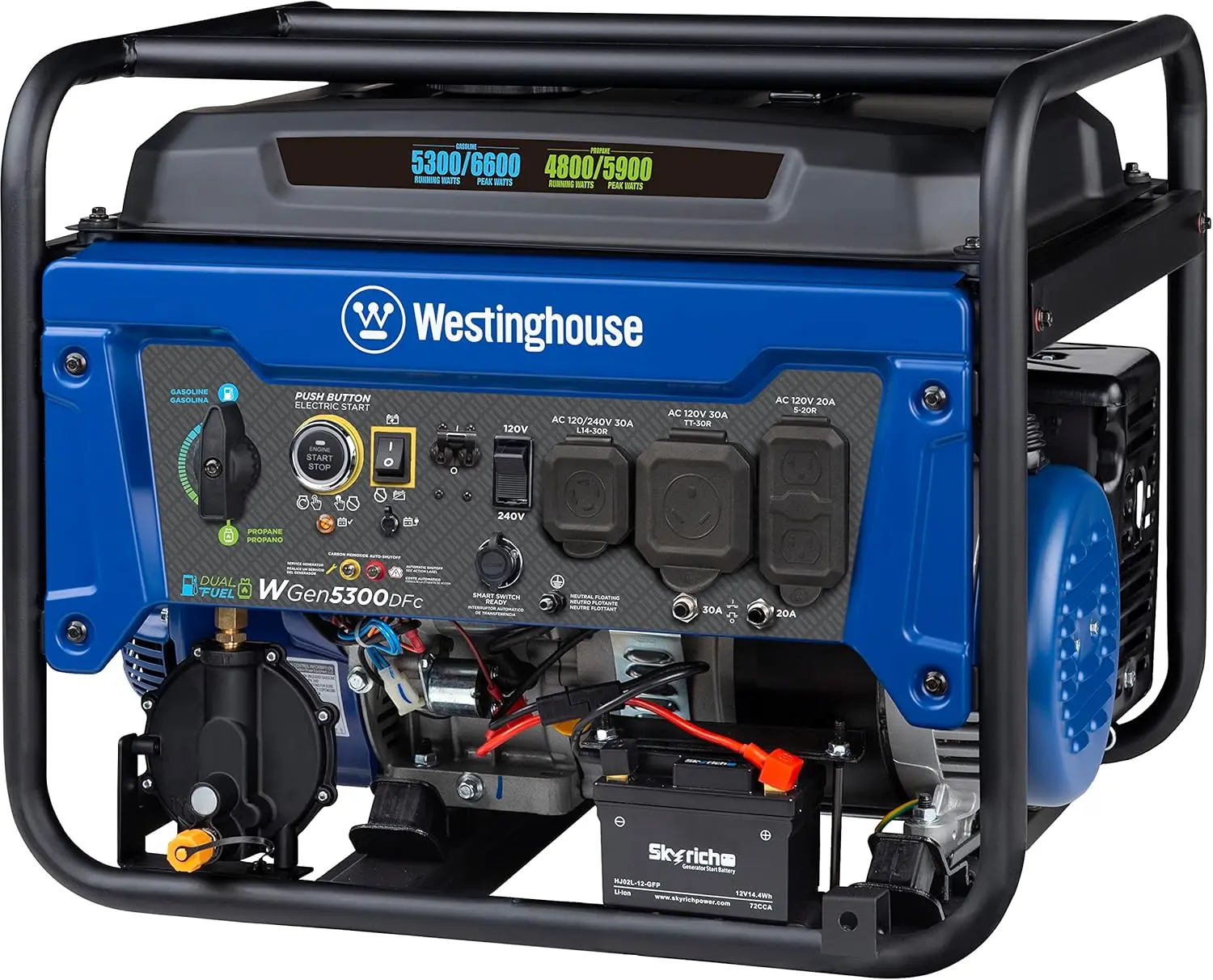
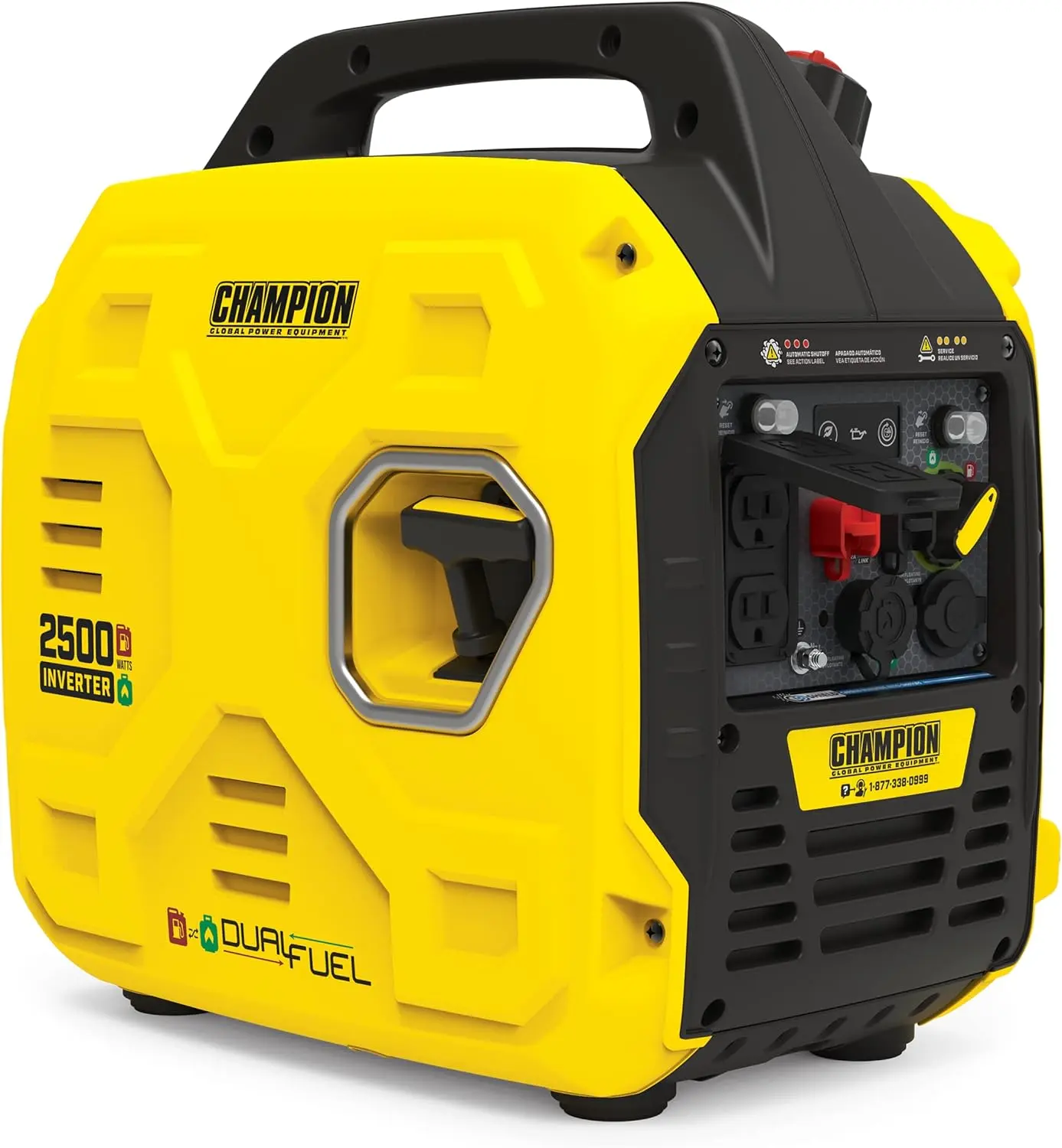
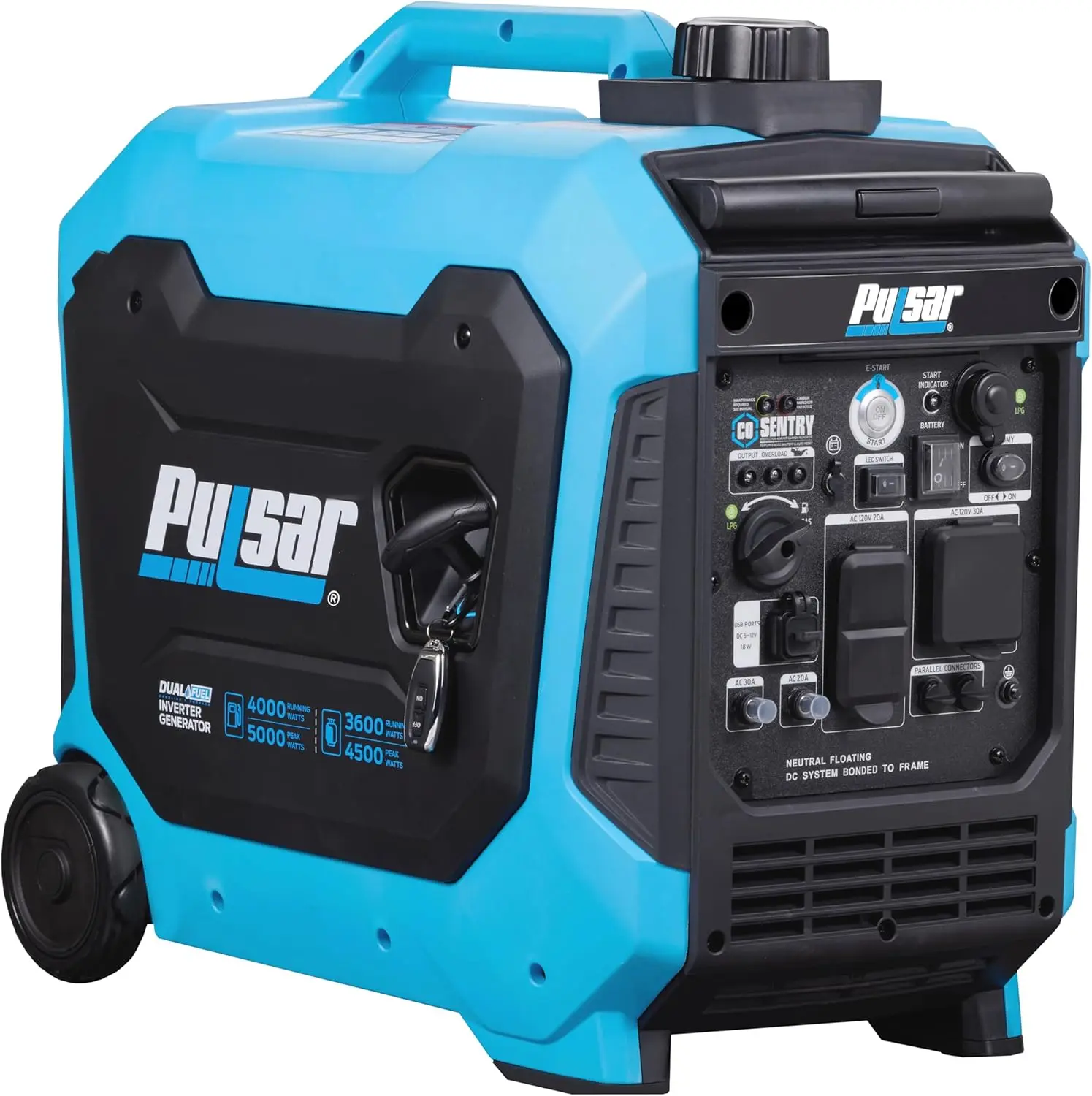
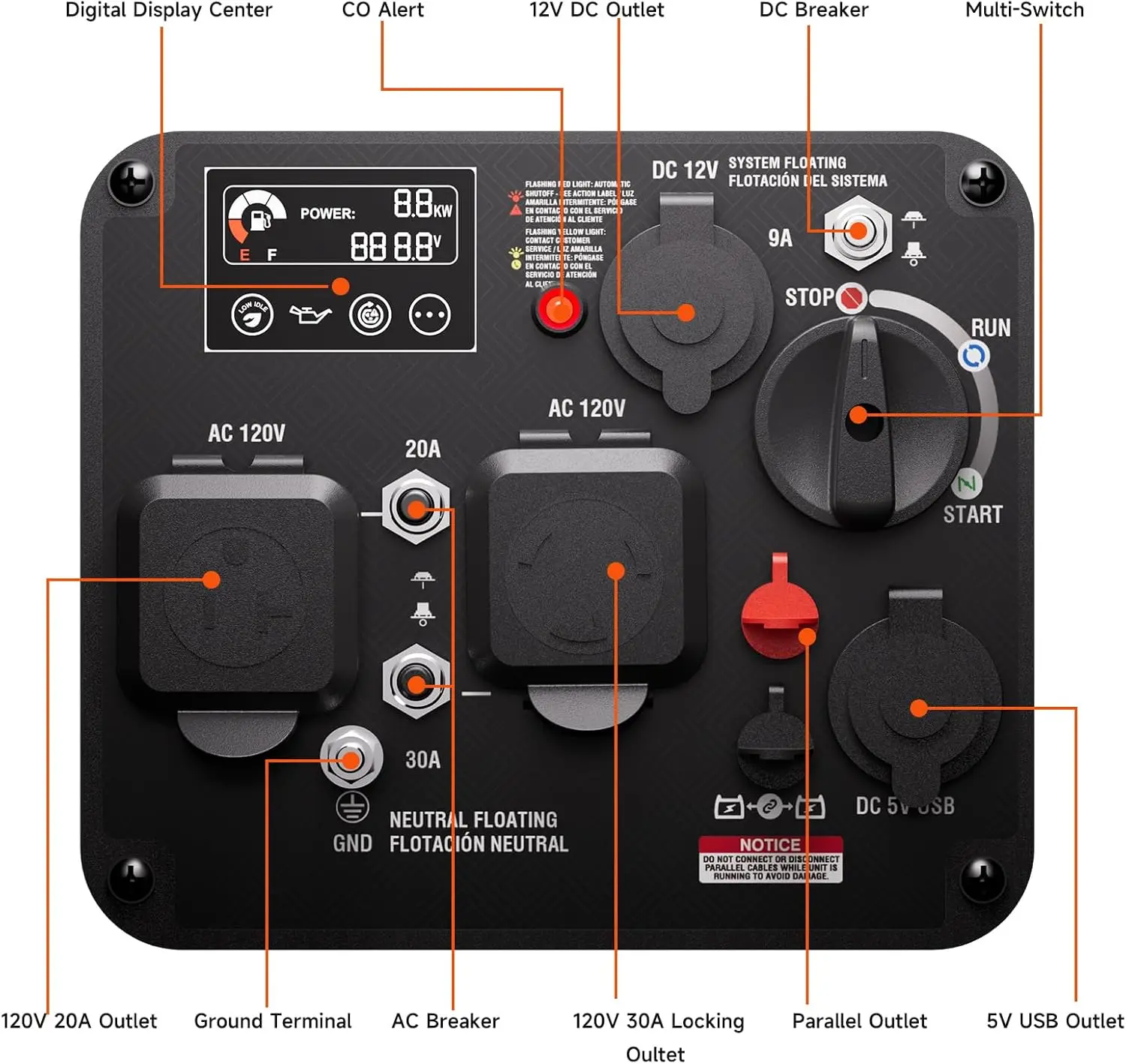
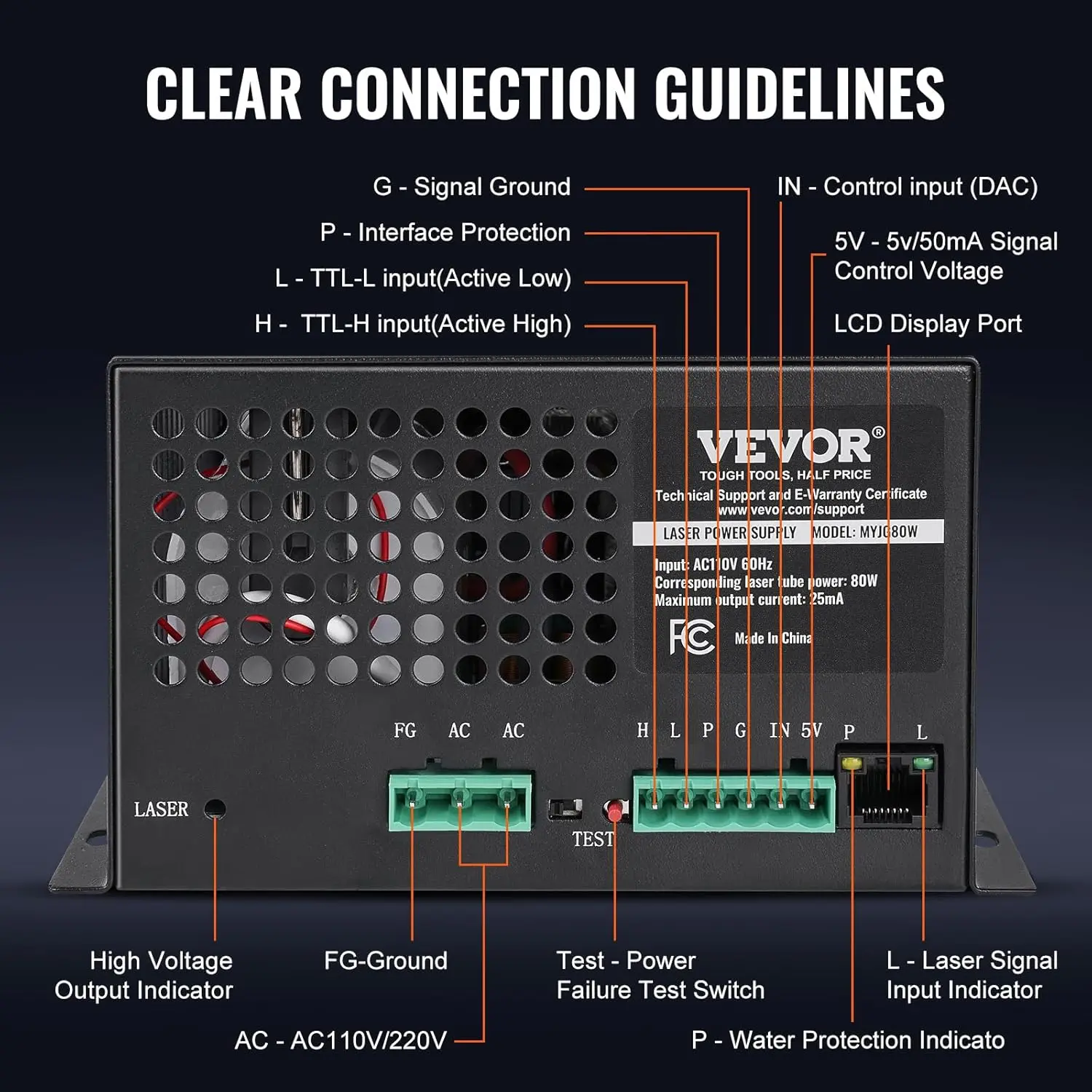
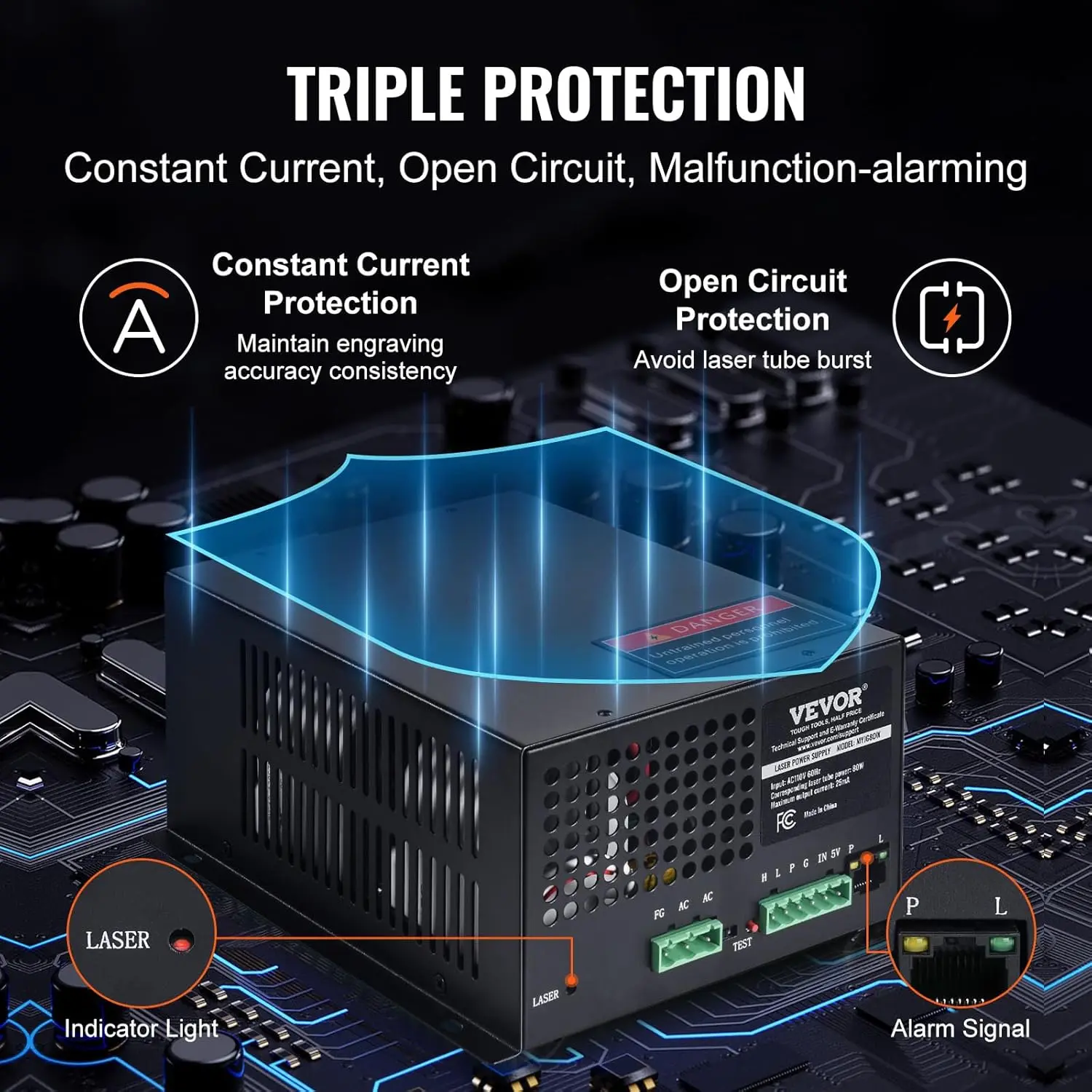
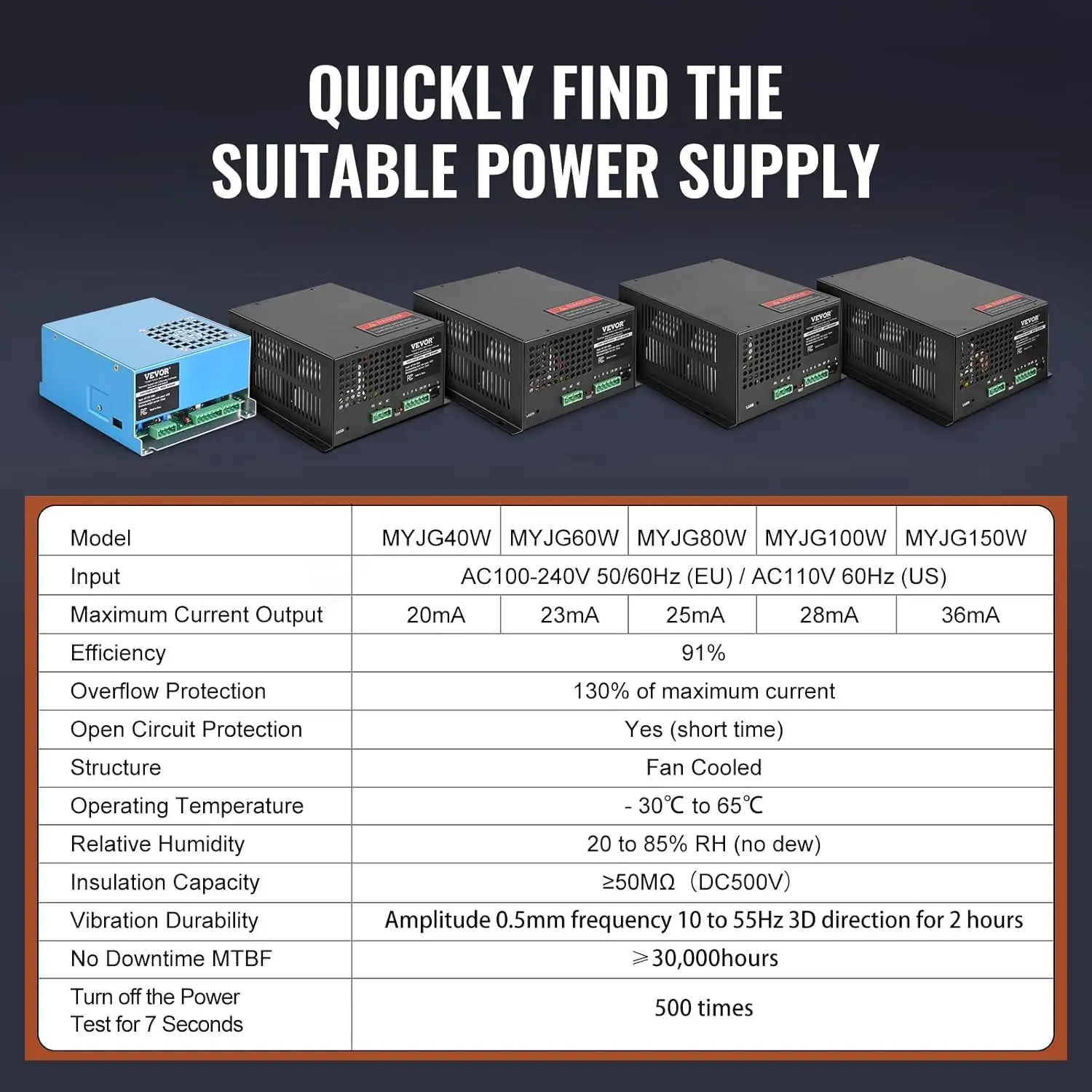
<p>Product name: DC reduction motor</p><p>Revolutions: 10-1280rpm</p><p>Current: 1A</p><p>Motor size: 37 * 52MM</p><p>Speed regulation: adjustable</p><p>Weight: 151g</p><p>Model: JGB37-520</p><p>Voltage: DC 6V12V24V</p><p>Power: 2W</p><p>Use for 24 consecutive hours</p><p>Output shaft size: 6 * 15MM</p><p>Forward and reverse: Yes</p><h1>Explanation of motor related parameter names</h1><h1><br/></h1><p>1. No load speed: the speed at which the motor is normally energized without load. (Unit: rpm or r/min or r/min)</p><p>2. No load current: the current of the motor under normal energization and no load state. (Unit: MA mA</p><p>3. Load torque: rated torque of motor during load test, only for test reference; (Unit: gcm g/cm or kgcm kg/cm)</p><p>4. Load speed: the speed of motor under load torque. (Unit: rpm or r/min or r/min)</p><p>5. Load current: current of motor under load torque. (Unit: mA mA or A A)</p><p>6. Locked rotor torque: also called starting torque, is the maximum torque standard that the motor can withstand. If the torque is exceeded, the motor will stop or lock up. (Unit: gcm kg/cm or kgcm kg/cm)</p><p>7. Locked rotor current: also called starting current, which is the maximum current when the motor stops due to locked rotor; (Unit: mA sea milliampere or A ampere</p>
$52.025
$32.51
- Category : Home Improvement
- Brand : pioneer_tools_store_store Pioneer Tools Store Store
Colors
Sizes
-
+
<p>Product name: DC reduction motor</p><p>Revolutions: 10-1280rpm</p><p>Current: 1A</p><p>Motor size: 37 * 52MM</p><p>Speed regulation: adjustable</p><p>Weight: 151g</p><p>Model: JGB37-520</p><p>Voltage: DC 6V12V24V</p><p>Power: 2W</p><p>Use for 24 consecutive hours</p><p>Output shaft size: 6 * 15MM</p><p>Forward and reverse: Yes</p><h1>Explanation of motor related parameter names</h1><h1><br/></h1><p>1. No load speed: the speed at which the motor is normally energized without load. (Unit: rpm or r/min or r/min)</p><p>2. No load current: the current of the motor under normal energization and no load state. (Unit: MA mA</p><p>3. Load torque: rated torque of motor during load test, only for test reference; (Unit: gcm g/cm or kgcm kg/cm)</p><p>4. Load speed: the speed of motor under load torque. (Unit: rpm or r/min or r/min)</p><p>5. Load current: current of motor under load torque. (Unit: mA mA or A A)</p><p>6. Locked rotor torque: also called starting torque, is the maximum torque standard that the motor can withstand. If the torque is exceeded, the motor will stop or lock up. (Unit: gcm kg/cm or kgcm kg/cm)</p><p>7. Locked rotor current: also called starting current, which is the maximum current when the motor stops due to locked rotor; (Unit: mA sea milliampere or A ampere</p>
Related Product
Browse The Collection of Top Products.